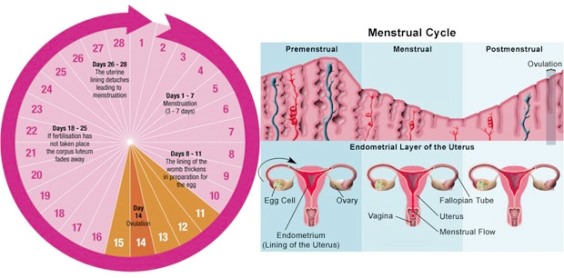
Overview
Menstrual problems are one of the most common gynecologic issues. Menstrual irregularities may result in a woman not getting her period, or having periods too frequently or infrequently. Other menstrual problems include unpredictable or excessive menstrual bleeding, or severe pain during menstruation.
Menstrual irregularities are usually a sign of an underlying medical issue. That’s why it’s important to see your physician if you’re experiencing any unusual changes in your menstrual cycle such as:
- Irregular menstrual cycles, which may include having a period more often than every 21 days, or less often than every 35 days, for several cycles
- Bleeding or spotting between periods; or bleeding or spotting after menopause;
- Menstrual bleeding that lasts for more than seven days
- Soaking through one or more pads or tampons each hour for several hours in a row
- Severe pain during menstruation
Types
There are four main categories of menstrual problems:
- Amenorrhea is a term used to describe the lack of menstruation. Amenorrhea occurs when a woman does not get her period by age 16, or when she stops getting her period for at least three months and is not pregnant.
- Oligomenorrhea is a term that refers to infrequent menstrual periods, or having a period only occasionally.
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding refers to either excessive menstrual bleeding (also called menorrhagia), or bleeding/spotting that occurs between periods or after menopause. It also includes a condition know as dysfunctional uterine bleeding, which is menstrual bleeding that occurs more often than every 21 days or farther apart than 35 days. DUB may also result in periods that last longer than seven days.
- Dysmenorrhea refers to painful periods, including severe menstrual cramps. Dysmenorrhea may be accompanied by other symptoms, including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache, or discomfort in the lower back.
Causes
- Amenorrhea (lack of menstruation) is not a disease, but a symptom of another condition. Possible causes can include: pregnancy, moderate or excessive exercising, eating disorders, physical or psychological stress, tumors, polycystic ovary syndrome, premature ovarian failure, menopause and thyroid or hormonal imbalances.
- Oligomenorrhea (infrequent menstruation) is also a symptom of an underlying medical condition. Possible causes can include: polycystic ovary syndrome; premature ovarian failure; uterine disease; disorders of the thyroid, pituitary gland or hypothalamus; and other hormone imbalances.
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding can occur as a result of many different types of conditions: fibroids or polyps; endometriosis; an infection; ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage; uterine disease; hormonal imbalances and use of certain medications. In menopausal and postmenopausal women, bleeding or spotting should be promptly evaluated by a physician.
- Dysmenorrhea (pain during menstruation) may occur as the result of the period itself, but it can also be caused by conditions like infection, endometriosis, fibroids, or ovarian cysts.
Treatment Options
To determine the cause of the problem, your physician will perform a thorough pelvic examination, discuss your symptoms and medical history, and in most cases order a Pap Test. In addition, your physician may also recommend other diagnostic tests such as pelvic ultrasound or laparoscopy to help further clarify or diagnose the cause of the problem.
When it comes to treating menstrual irregularities, there are many options depending on the cause of the problem. Some of the most common treatment options include:
- Treatment of Amenorrhea (lack of menstruation) depends on the underlying cause. Sometimes lifestyle changes can help if weight, stress, or excessive exercise or physical activity is causing amenorrhea. Other times, medications and oral contraceptives may be prescribed to resolve the problem.?
- Treatment of Oligomenorrhea (infrequent menstruation) is generally a symptom of an underlying medical condition. Treatment depends on the cause of the problem. Many causes can be treated with hormonal therapy or oral contraceptives. Athletes whose menstruation is off because of their diet or exercise level may need to vary their fitness plan to regulate their periods. Women who develop oligomenorrhea because of an eating disorder require assistance from a nutritionist and therapist. If oligomenorrhea is the result of a tumor, surgery may be required.
- Treatment of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding depends on the cause of the problem. In the case of excessive bleeding (menorrhagia) or dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB), treatment options may include hormonal therapy, dilation and curettage (D&C), hysteroscopic procedures to remove polyps, and endometrial ablation or resection. In the case of bleeding or spotting between periods, treatment varies and may include hormonal therapy and treatments to resolve infection or inflammation. In menopausal and postmenopausal women, bleeding or spotting should be promptly evaluated by a physician.
- Treatment for Dysmenorrhea (pain during menstruation) depends on the underlying cause. For mild cases not related to an underlying health issue, medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help to relieve pain and uterine contractions. Oral contraceptives and the use of an IUD can also help to reduce painful periods. In the case of pain resulting from an underlying condition such as fibroids or endometriosis, there are several treatment options available depending on the severity of the problem, including non-surgical options such as endometrial ablation and minimally-invasive laparoscopic surgery.


























































 Address 1
Address 1
